First of all, Check your Welding Machine
Before a new welding work is started, the operating status of the welding machine must be checked. Check for:
- The connections of the power cable, gas line pipe, grounding cable and welding torch must be checked.
- It must also be ensured that the correct type of shielding gas is used and that the gas outlet is working.
- The type and thickness of the welding wire must be checked.
- Furthermore, it must be ensured that the wire spool is correctly installed in the wire feeder. Thereafter, the drive rollers of the motor of the wire feeder must be checked, ensuring that the wire guides and drive rollers are suitable for the filler material and wire diameter used.
- The welding torch must be detached from the wire feeder, ensuring that the size and type of wire feeder are correct. The gas nozzle must be removed from the torch and cleaned.
Without a wire feeding (just loose the wire feed rollers so they will not push the wire) in the torch, the shielding gas flow can be tested with a gas flowmeter.

If the wire is already in the welding torch, the pressure adjustment screw of the motor of the wire feeder must be loosened so that the wire cannot move. Then the torch button is pressed and the gas flow is measured.
The easiest way to check the shielding gas flow is to use the GAS TEST function, if this function is available in the wire feeder. This function only activates the gas flow to the welding torch, but not the wire feeder.
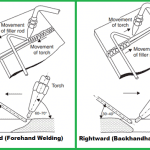
Welding angle and Torch Guide
When welding with solid or cored wires, the torch is usually guided by the handle behind the direction of movement, except for downward welding and welding of particularly thin sheets.
In symmetrical fillet welding, the welding torch is to be held at a 45-degree angle to the weld throat corner.
Welding torch travel speed
The correct welding travel speed is an important factor for successful welding. The travel speed influences the shape, penetration, heat input and effective size of the weld.
The effective fillet weld throat size refers to the shortest distance from the foot to the surface of the weld.

If the speed of movement is too slow, the weld pool can soon be in front of the arc and the liquid weld pool is difficult to handle.
On the other hand, an excessively travel speed can lead to too little penetration depth and too little effective fillet weld size.
The recommended travel speed can be found in the welding instructions. However, it is difficult to estimate the speed during the welding process.
One way to determine the speed is to weld about 10 cm and record the time it takes. This makes it possible to determine the speed in inches per minute or centimeters per minute.
Delay arc Startup function
At high wire feed speeds, it can be difficult to start the welding process. A so-called delay start function has been set up to make it easier to start the welding process.
With the help of the delay function, the wire feed starts at low speed and does not reach the preset value until the wire touches the workpiece and the current flows. If required, the delay value can be set on the operating panel of the welding machine.
Hot Start and Soft Start
When welding materials with good thermal conductivity, such as aluminum, mistakes can easily be made at the weld seam at the beginning.
These errors can be reduced with the help of the hot start function.
Due to a hot start, the welding performance briefly increases to a level above the preset welding performance at the start of welding. The power and duration of a hot start can usually be set on the machine’s control panel.
When welding square butt joints of sheet metal, the so-called soft start function can be useful, as it helps to keep the edges of the sheets intact.
Soft start is the opposite of hot start. With soft start, the welding power at the beginning of welding is briefly lower than the actual welding power. The power and duration of a soft start can usually also be adjusted via the machine control panel.
Setting MIG welding parameters
In MIG welding, the wire feed speed and the welding current are inter-connected. Changing one parameter will automatically adjust other reciprocating value.
As the wire feed rate is increased or decreased, the welding current got adjusted automatically due to machine CV characteristics.

The arc voltage must be correctly related to the wire feed speed and the welding current. However, sometimes it can be very difficult to decide which value to change in which direction in order to achieve good welding results.
Following are useful tips to select correct welding voltage and current in MIG Welding:
The arc voltage is too low with respect to the wire feed speed if:
– the sound of the arc is too loud.
– excessive spatters are produced.
– the weld seam is narrower and higher than it should be.
The arc voltage is too high with respect to the wire feed rate if
– the sound of the arc is quiet/soft.
– the arc is long.
– the weld seam width is wider and lower than it should be.
– the drops of the filler material are large.
There are several tables and guides that are helpful for achieving good welding results. There are also welding machines that automatically determine the correct arc voltage for wire feed speed and welding current.
However, even with such machines, it may be necessary to adjust the arc voltage because there may be differences in the welding wires of the various manufacturers. ´
Sometimes it may be impossible to set the arc voltage exactly to the correct number with respect to the wire feed speed. In such cases, fine tuning can be done by increasing or decreasing the wire feed speed and making trial run.
Common tips for improving welding work
There are simple methods to improve welding work. With manual work steps that have been appropriately planned and ergonomically designed, individual welder can experience higher productivity increases than would be possible through mechanization.
Attention must be paid to the working posture. The most effective posture for welding is the flat position.
In flat position welding, the workpiece is set to a level that allows welding in a natural position.
In addition, devices should be used to rotate the workpiece so that the position of the workpiece allows ergonomic welding.
Material Welding is run by highly experienced welding engineers, welding trainers & ASNT NDT Level III bloggers.
We strive to provide most accurate and practical knowledge in welding, metallurgy, NDT and Engineering domains.