What is Catalytic Conversion?
Catalytic conversion is an important process used to reduce hazardous emissions from vehicles and other sources.
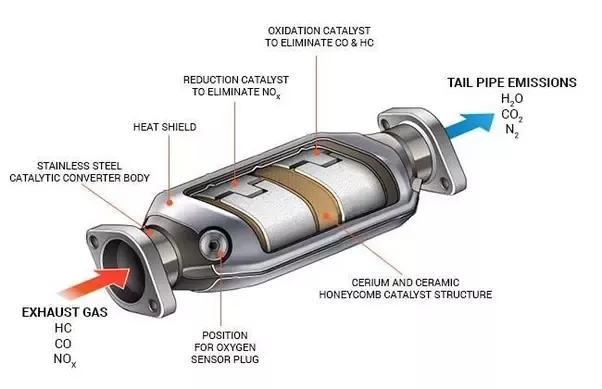
It uses a catalyst to convert toxic substances, such as carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into less harmful emissions like carbon dioxide, nitrogen gas and water vapor.
This process helps reduce air pollution in urban areas and makes the air safer for people to breathe.
What is a Catalytic Converter?
Catalytic converters are commonly found in cars, trucks, buses, and some heavier equipment that run on gasoline or diesel engines.
The catalysts used in these converters typically consist of platinum or palladium metals coated onto ceramic beads which act as a filter for exhaust gases.
It works by causing chemical reactions between the gases passing over it, allowing the pollutants to be broken down into new compounds. The result is that exhaust gases are significantly reduced in toxicity levels before they are released into the atmosphere.
Catalytic converters also help improve engine efficiency and performance by reducing back pressure from clogged exhaust systems.
These catalysts speed up the reaction between pollutants found in the exhaust system so that when they enter the atmosphere they are not as harmful as before being treated by the converter.
What Does Catalytic Conversion Mean in Refinery?
Catalytic conversion is a process used by refinery operations to convert heavier fuel hydrocarbons and chemicals into lighter ones. This process is highly beneficial to the environment because it helps reduce the production of pollutants from fuel consumption.
By using catalysts, refineries are able to break down heavier molecules and reconfigure them into lighter ones, allowing them to be burned more efficiently in engines and other machinery.
The use of catalysts in this conversion process also makes conversions more efficient as they help speed up chemical reactions without being consumed during the reaction themselves. In addition, catalysts can increase yields of desired compounds by optimizing the balance between reactant concentrations and temperatures. By using catalysts, refineries are able to make environmentally friendly light fuels from heavy feedstocks with greater efficiency than ever before.
Catalysts Types
The catalysts used in this conversion process can be either organic or inorganic. Organic catalysts are typically derived from natural sources such as wood chips or sawdust, while inorganic catalysts are usually synthesized from metals like platinum or nickel. The type of catalyst selected will depend on the specific application and desired result of the end-product fuel.