Ultrasonic Welding of Plastics
Ultrasonic welding is a form of plastic joining that uses high frequency sound waves to join two pieces of thermoplastic material together.
This joining process relies on the energy created by the sound waves to create enough heat and pressure to melt the two parts together.
In ultrasonic welding, a sound wave is sent through the upper half of the product in the direction of the partial seam.
The result is a strong and permanent bond that can be used for various applications, including automotive, medical, electronics and consumer products.
In ultrasonic welding, the process times are very short, often shorter than 1 second.
How ultrasonic plastic welding works?
In ultrasonic welding, high-frequency vibrations are applied to two parts by an oscillating tool, commonly referred to as a “Horn”. The welding is carried out by the heat generated at the interface between the parts.
The ultrasonic vibrations are generated by a series of components –
- Transducer,
- Converter,
- Booster,
- Horn – that transmit mechanical vibrations to the parts.
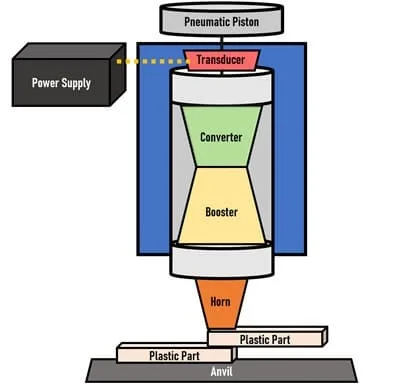
The generator (Transducer) takes a standard electrical mains voltage (e.g., 230 V/ 50 Hz) and converts it into an operating frequency. This electrical energy is sent to the converter via an RF cable.
The converter uses piezoelectric ceramics to convert the electrical energy into mechanical vibrations with the operating frequency of the generator.
This mechanical vibration is either amplified or decreased depending on the configuration of the booster and the horn device.
In below video, you can see the animation for Ultrasonic welding principle.
The correct mechanical vibration, known as amplitude, is typically determined by an application engineer and is based on the materials to be welded.
The parts to be welded are mechanically vibrated and subjected to mechanical force, usually with a pneumatic actuator.
Under this load, the mechanical vibrations are transmitted to the interface between the parts, where they are focused on a triangular bead, the energy director, which bundles the vibration to create intramolecular and surface friction. This friction generates heat and a subsequent melt that solidifies into a welded joint.
Ultrasonic Welding of Plastic & Composite steps
The steps of Ultrasonic welding are:
- Connection of an electric ultrasonic oscillation generator with a frequency of 20,000 Hz.
- Conversion of these vibrations into mechanical longitudinal oscillations using a special transducer.
- The connection of the longitudinal-oscillating waveguide is perpendicular to the welded joint to input the already converted oscillation energy.
The following processes occur during the welding operation:
- The transition of mechanical energy to wave energy, which is accompanied by a rapid heating of the contact zone of the waveguide and the material to the fluid state of the second. In doing so, the waveguide provides the proper conditions for heating materials and for precise energy concentration due to the applied static pressure.
- In turn, the applied dynamic force is provided by the oscillation of the waveguide itself and acts to increase the temperature of the heating zone.
Ultrasonic Welding Machine
Ultrasonic welding of plastic is carried out using special machines. An Ultrasonic welding machine contain the following parts:
- Power supply.
- Oscillatory mechanical system.
- Control equipment.
- Pressure drive.
The oscillatory system is used to convert electricity into a mechanical one for its subsequent transmission to the connection site, concentrating it and obtaining the required value of the emitter speed. This node contains:
- Electromechanical transducer with windings. It is enclosed in a metal case and cooled by water.
- Elastic oscillation transformer.
- Welding tip.
- Support with pressure mechanism.
Ultrasonic Welding Machine Parameters
Ultrasonic Welding Machine Parameters are:
- Ultrasonic welding pressure.
- Pulse duration.
- Sonic Wave pressure on the material.
- The number of oscillations per unit of time (frequency).
- The range of oscillations of the end of the wave.
- Additional: temperature mode of heating of the material, parameters depending on the characteristics of the parts themselves (for example, size and / or shape), etc.
Ultrasonic Welding frequencies
In ultrasonic welding, the frequencies used are 20, 30, 35, 40 and 70kHz. The higher the frequency, the smaller the maximum dimensions of the product. Because a defined weld seam horn is required, the method is especially suitable for injection molded products.
The process must be adapted to the material used. For each material type, a different optimal amplitude of the ultrasonic wave applies.
Measurements have shown that the temperature of the horn can reach several hundred degrees. This makes plastic joining by ultrasonic welding the fastest welding method.
For each ultrasonic welding head, the maximum dimensions at 20 kHz are limited to 400 x 5 mm or 220 x 220 mm. Welding larger products requires the use of different ultrasonic heads and a special machine.
Ultrasonic Plastic Welding cycle time
Perhaps the biggest factor in the adhesive assembly process is the required cycle time. Thus, the cycle of adhesive assembly is not finished when the two parts are brought together.
An adhesive bond requires a curing time for each part. Ultrasonic welding, on the other hand, provides a durable, welded connection in a second or less.

As soon as the welded part is removed from the welding tool, the welding cycle is complete. A new part can be loaded and welded immediately.
When selecting materials, the joining methods of bonding and ultrasonic welding differ- it is generally more difficult to bond different materials – rubber with plastics or plastics with metals, for example.
Mechanical fasteners are more suitable here. Ultrasonic welding is the ideal solution for welding nonwoven textiles, such as face masks or medical garments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding
The main distinguishing features of ultrasonic welding of plastics and polymeric composites are the ability to weld on surfaces contaminated with various products, local heat generation in the welding zone, which eliminates overheating of plastic.
The main Advantages and Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Welding are:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| – No consumables | – Requires capital investment |
| – Line production | – Specific common design (energy directional encoder) required |
| – Easy setup and fast cycles | – Welding energy can affect sensitive components |
| – High-strength connections | – Usually requires dedicated tools |
| – Minimal device maintenance | – Limited to specific component geometries/contours |
| – Easy integration into automation | – Noise; depending on frequency and part size |
Can you ultrasonic weld plastic to metal?
Ultrasonic welding works best when both the plastic and the metal have similar properties in terms of thickness and shape so that they fit together snugly.
Can polypropylene be ultrasonic welded?
What is sonic welding of plastic?
The most common type of sonic welding consists of an ultrasonic generator connected to a horn that transmits pressure and energy to the plastic parts being welded. The process can be used on thermoplastics such as polypropylene, polyethylene, ABS, nylon and PVC in order to join them into one piece.





