Welding Process Classification based on the degree of Mechanization
Welding processes are usually classified by the degree of mechanization by the code (E.g. ASME Section IX or AWS D1.1) and standards ( e.g. ISO 9817, ISO 15614-1). This classification is basically founded on the manual efforts put by the welder or operator during the welding processes.
The classification is based on the various parameters such as movement of the welding torch, feeding of electrode or filler wire, and the handling of the workpiece. There are four main types of welding processes based on this classification:
- Manual Welding
- Semi-automatic welding
- Fully-mechanised or Machine Welding
- Automatic Welding

Manual Welding
Manual welding is designated as (m) according to ‘DIN-1910: Welding and allied processes – Vocabulary – Part 100: Metal welding processes’ or DIN EN 14610:2005.
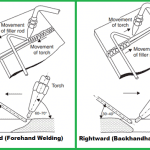
In Manual Welding operation, the complete welding operation is controlled by the hand during the welding. The feeding & guidance of the electrode, travel of the torch, and the handling of the workpiece.
SMAW or stick welding is an example of a manual welding operation as shown in the below picture. Semi-automatic variants of the SMAW are also available such as spring tension SMAW welding although their applications are very limited.

Semi-Automatic Welding
In semi-automatic welding operation, the welding torch or gun movement is manually controlled by the welder but the electrode feed is automatic & the workpiece is handled manually. For example, in MIG-MAG or FCAW welding.
The welder only moves the torch during the welding and the welding wire is fed automatically from the wire feeder connected to the welding machine.
So, the welder is only responsible for the torch movement and workpiece handling. An example of a semi-automatic process is shown in the below picture.
Fully-mechanised or Machine Welding
In mechanized welding, the welding current, welding voltage, and welding speed parameters are set to fixed values via the controls (torch movement, workpiece movement, and wire feed) on the welding machine without the manual movement by the welder.
Similarly, machine welding is defined as the type of welding where the welding operators control the welding via the controls (by adjusting torch movement, workpiece movement, and wire feed via buttons) on the welding machine. Hence, the welder or operator does not engage in manual handling of the welding torch & wire feed.
An example of machine welding or fully mechanized welding is Submerged Arc Welding where the welder controls welding torch movement & wire feed via machine buttons.

The following welding variables are controlled in mechanized welding machines:
- Initiation and control of the welding arc,
- Feeding the welding electrode wire into the arc, and
- Travel speed and work-piece rotation.
Controlling the welding speed, weld direction, and uniform feeding is very important for good quality. Any wrong travel path, unnecessary torch oscillation, and uneven travel speed could cause deterioration of weld output and can affect the welding bead appearance and quality.
GMAW as well FCAW can be fully mechanized conditional to setting up special purposes machine called SPM, where the torch movement is synchronized with the welding machine and controlled by electronic buttons.
They are very useful for mass production where the torch is fixed on a lathe and circular seams are welded. Other welding systems are used in pipeline welding using special-purpose welding machines using GMAW and FCAW processes.

Robotic Welding
Robotic welding is a type of welding where torch movement, wire feed as well as workpiece handling are automated. The welding operator uses the machine controls to control all the welding parameters. In robotic welding, the welding parameters are programmed in the machine and can be recalled for a later stage.
The handling of the welding parts is automated too and no manual operation is involved. A summary of the main parameters that define the degree of welding automation is given in the below picture.


Dr. Sandeep Kumar
Hi, I'm Dr. Sandeep Kumar. I am a passionate Welding & Material Expert with a Ph.D. and M.Sc. in Welding Engineering. As an International Welding Engineer (IWE), I bridge the gap between academic research and practical industrial application. My goal is to share high-level knowledge on metallurgy, welding technical knowledge, and engineering best practices to help professionals and students succeed in the field.