Resistance Spot welding
Resistance Spot welding (RSW) is a type of resistance welding. The feature of Resistance spot welding is welding at one or more specific points, which makes it possible to simply weld thin metals.
The strength of welding directly depends on the size and structure of the welding point. This is determined by several factors, including the condition of the welded surfaces, the shape and size of the electrode used, the parameters of the welding current, the applied forces and others.
During welding, when the base materials are electrically conducted, the pressed part generate resistance between both faying surfaces, and heat is generated, and the base material melts and sticks. Spot welding is also called resistance spot welding (RSW).
It is usually performed by pressing two electrodes and is applied to sheet materials with a thickness of 0.5~3 mm. Electrodes of copper alloy are used and melted through high currents. The advantage of this method is that a large amount of energy can be used for a very short time (about 10~100 msec.) It has the advantage that other parts of the base material except the weld do not heat up.
(Immediately after arc welding, the base metal is too hot to touch, so be careful.)
It is often used for plate welding, and a typical example is automotive car welding.
Resistance Spot welding Technique
Resistance Spot welding is based on the simple principle of obtaining a welding joint by compressing parts by pressure and melting the contact area due to electric resistance heating.
First of all, it is necessary to thoroughly clean the welded parts from any possible contaminants. After preparation, the parts are placed between the contact electrodes.

In the process, an electric current passes through metal parts from one electrode to another. Due to the high electrical conductivity of the alloy used for the electrodes, the minimum current resistance at the point of contact of the electrode and the part is ensured, while the resistance between the two parts reaches a maximum value.
Due to the thermal effect of the current according to the Joule’s first law, the metal of the parts is heated and melted. After that, the parts are pressed with high pressure. The connection point as a result forms a welded point called Weld Nugget, the diameter of which can be from 4 to 12 mm, depending on the strength of the acting current.
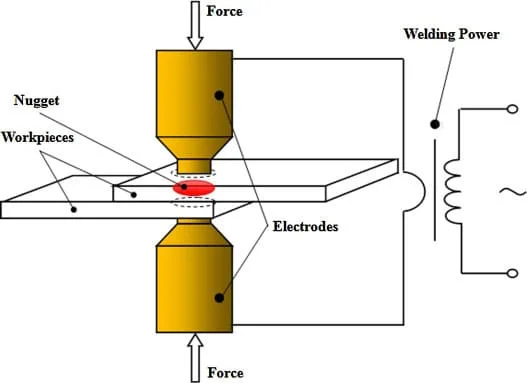
Resistance Spot welding Process features
In electric arc welding, the melting of the contacted metal is achieved due to the high temperature of the electric arc.
Resistance Spot welding is radically different in that the open arc is not ignited – the parts are compressed by special welding pliers through which the current passes.
It heats the metal in the places of contact with the electrodes, which also mechanically compress the parts – a kind of “hot rivet” of heated and softened areas of metal is obtained, but in a limited area (at the point).
Thus, spot welding is characterized by the following features:
- very high operating current (over 1000 A);
- short connection time (no more than a few seconds);
- very low operating voltage (not more than 10 V);
- high clamping force of ticks (tens and hundreds of kilograms).
In accordance with this, the technology is used mainly for connecting overlapping sheet metal blanks of a large area. According to the thickness of the workpieces, spot welding is possible for sheets from micrometers to 2-3 cm. But the most popular area is the welding of sheets 5-6 mm thick.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of Resistance Spot Welding are:
- The main advantage of spot welding is efficiency – both in terms of the time of a single operation, and in terms of energy costs, and the absence of consumption of auxiliary materials (flux, electrodes, etc.).
- Due to the heating of the metal only in a small area, residual deformation does not form in the parts.
- Also, the seam turns out to be neat – there is no scale, blackening of neighboring areas of metal, etc.
- Spot welding equipment is very simple and compact.
- During operation, harmful gases are not released or formed – the welding process is environmentally friendly.
- Spot welding is perfectly amenable to automation.
- RSW gives neat and smooth connections with high strength,
- High level of process automation,
- high environmental friendliness and almost complete absence of waste in the process,
Naturally, this method of welding has drawbacks:
- No leakproof welds.
- The welding point acts as a concentrator of internal stresses (however, this drawback is easily eliminated by simple technological techniques).
Resistance Spot welding Parameters
Spot welding parameters include:
- Current;
- the duration of the current pulse;
- clamping force of tick electrodes;
- geometric dimensions of contact electrodes (these can be spheres – then their radius is estimated, or flat surfaces – then their area becomes key).
Since the process proceeds quickly, it is usually not static values that are evaluated, but their dynamic change according to special programs.
Resistance Spot welding Applications
Resistance spot welding is a common and efficient method of joining two or more metal sheets together.
In automotive manufacturing, resistance spot welding is often used in assembly lines for attaching components such as door panels, fenders, trunk lids and other body parts.
Sheet metal fabrication also uses this process for creating many different shapes from sheet metal stock.
In addition, this process can be used for creating packages that are useful for containing electronic components and other items. It can also be used in joining wire mesh products such as grills or perforated metals.





